About Arthritis
As the nation’s #1 cause of disability, arthritis affects nearly 60 million adults and 300,000 children. Over 100 types of arthritis and related conditions damage the joints and often other organs.
How can we assist you?
Helpful Tools for You
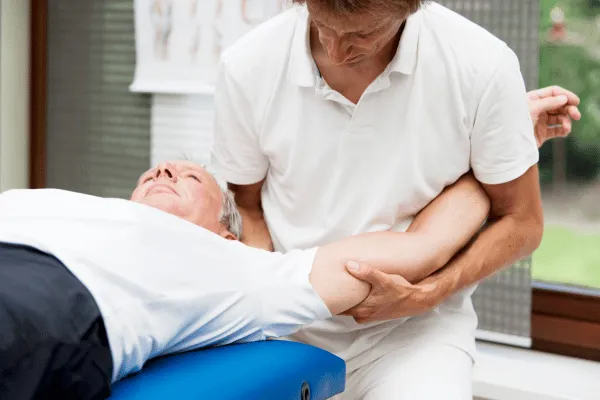
Osteoarthritis of the Shoulder
Shoulder osteoarthritis (OA), sometimes referred to as degenerative joint disease, is a condition where the cartilage and joint tissues experience gradual wear and tear. This can lead to increased friction in the joint, resulting in discomfort and a potential reduction in movement and functionality. While shoulder OA isn't as prevalent as OA in the hip or knee, it's believed that about 1 in 3 individuals over the age of 60 may have some degree of shoulder OA. It's always a good idea to be aware and seek guidance if you have concerns.
Joints in the Shoulder
Did you know that your shoulder consists of three bones which create two distinct joints? The first joint, known as the acromioclavicular (AC) joint, is where your collarbone connects with the tip of your shoulder blade. The second one, the glenohumeral joint, is where the top of your upper arm bone slots into your shoulder blade. Interestingly, OA tends to be more prevalent in the AC joint compared to the glenohumeral joint.
Causes of Shoulder OA
Shoulder osteoarthritis (OA) can be categorized into two types: primary and secondary. Primary OA doesn't have a pinpointed cause but often relates to factors like age, genetics, and gender. Typically, individuals over 50, especially women, may experience it more frequently. On the other hand, secondary OA arises from identifiable reasons, like past injuries, shoulder dislocations, infections, or issues with the rotator cuff. Engaging in demanding professions, such as construction, or certain sports activities can also increase the likelihood of developing shoulder OA. It's essential to be informed and take care of our joints.
Signs of Shoulder Osteoarthritis
Shoulder arthritis often presents itself with discomfort as its primary sign. Typically, activities might intensify this discomfort, and over time, the pain can increase. As the condition advances, you may even notice this discomfort during rest or when trying to sleep. The exact location of the pain largely depends on which shoulder joint is affected:
For the glenohumeral shoulder joint: The discomfort is typically felt at the back of the shoulder, resembling a deep, persistent ache.
For the AC joint: The pain is more concentrated on the top of the shoulder and can sometimes spread up the side of the neck.
Additional symptoms to be aware of include:
Limited Movement & Stiffness: This can result in a decreased range of motion, potentially making everyday activities, like reaching overhead or washing your hair, a bit challenging.
Crepitus: This is characterized by a grinding or clicking sensation or sound when you move your shoulder.
Exploring Shoulder OA Diagnosis
To determine if you have shoulder OA, your physician will discuss your symptoms and delve into your medical background. During this evaluation, they will assess:
Your muscle strength.
Any sensitivity when touched.
Your joint's flexibility includes both self-initiated and assisted movements.
Any indications of recent or past injuries.
Signs of arthritis in other joints.
Any grinding feeling within the joint during motion.
Discomfort when positioned in certain ways.
Potential swelling or an increase in joint size.
Following this assessment, it's common for the physician to recommend X-rays. These can reveal typical OA signs such as reduced joint space, bone modifications, and the emergence of bone spurs.
Exploring Therapies for Shoulder Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a long-term condition, and while there isn't a definitive cure, there are numerous strategies to alleviate discomfort, maintain movement, and keep active. Embracing a healthy lifestyle and self-care routines can be potent, natural ways to manage its symptoms. Consider exploring treatments like warm or cold packs, strength and flexibility workouts, physical therapy, supportive braces, and even massage.
There are a variety of medication options to soothe the symptoms of OA. These come in forms like tablets, liquids, topical creams, or direct joint injections. Some of these are pain-relief medicines such as acetaminophen, anti-inflammatory agents like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and even soothing agents like capsaicin or menthol.
If other treatments don't yield the desired results, surgery might be a consideration. This could involve procedures to clear out loose cartilage or bone fragments or even replacing damaged joints with durable materials like ceramic, plastic, or metal.
Effects of Arthritis

Cause of Disability
In the United States, 23% of all adults, or more than 54 million people, have arthritis. It is a leading cause of work disability, with annual costs for medical care and lost earnings of $303.5 billion.

Workforce Effects
Sixty percent of US adults with arthritis are of working age (18 to 64 years). Arthritis can limit the type of work they are able to do or keep them from working at all.

Global Impact
In fact, 8 million working-age adults report that their ability to work is limited because of their arthritis. For example, they may have a hard time climbing stairs or walking from a parking deck to their workplace.
Promoting Interventions That Reduce Arthritis Pain
American Arthritis Foundation recognizes several proven approaches to reduce arthritis symptoms:
Be active. Physical activity—such as walking, bicycling, and swimming—decreases arthritis pain and improves function, mood, and quality of life. Adults with arthritis should move more and sit less throughout the day. Getting at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity each week is recommended.
Protect your joints. People can help prevent osteoarthritis by avoiding activities that are more likely to cause joint injuries.
Talk with a doctor. Recommendations from health care providers can motivate people to be physically active and join a self-management education program. Should your arthritis be interfering with your activities of daily living you may be a candidate to receive many new treatments, and learn how to reverse the arthritis condition.
Have a question?
We're Here to Help
By providing my phone number, I agree to receive text messages from the business.


